Globally, the 3D cell culture market is witnessing high growth due to factors such as rise in research and development investments, higher adoption, use of microfluidic technology, increasing focus on regenerative medicine, and use of 3D cell culture models for drug discovery and toxicology in vivo testing. In addition, rapid increase in the need for organ transplantation is further expected to propel the growth of this market in coming years. However, the budget restraints by laboratories, lack of experienced professionals, and lack of consistency in 3D cell culture products, cost and complexity, and ethical concerns using animal sources are affecting the growth of this market.
Based on technology, the 3D cell culture market is segmented into scaffold-based and scaffold free systems. The scaffold-based segment is expected to account for the largest share of the global 3D cell culture market in 2016 and is expected to be the fastest-growing segment. Further development of advanced technologies and availability of innovative biodegradable and bioabsorbable materials are favoring the growth of scaffold free technologies in coming years.
Download PDF Brochure:https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=191072847
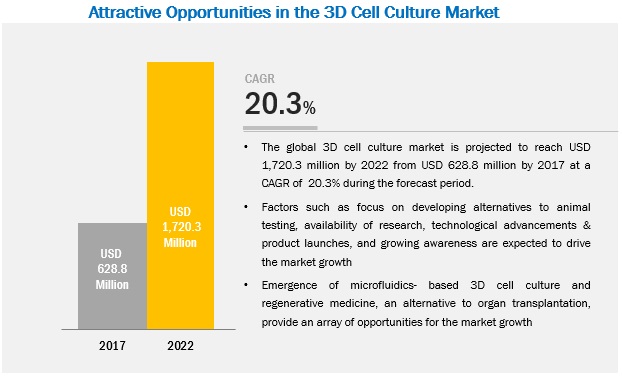
Based on application, the 3D cell culture market is segmented into cancer cell research, cell based assays/toxicity screening, regenerative medicine/tissue engineering, in vivo applications for stem cells, 3D printing/microfluidics, and others. The cancer cell research segment is poised to witness the highest growth rate in this market due to their increasing adoption as it speeds up the cancer drug discovery process than traditional time-consuming and expensive animal models.
Based on end-user, the 3D cell culture market is segmented into research laboratories & institutes, biotechnology & pharmaceuticals, hospitals & diagnostics centers, and others. The biotechnology & pharmaceuticals segment is poised to witness the highest growth rate in this market due to increasing healthcare expenditure and government investment.
In coming years, regenerative and stem cell research market offer huge potential to the growth of this market. Major players are developing advanced assay kits which will reduce the cost and efforts required in the field of regenerative medicine research such as identification of diseases pathways, and evaluation of potential new drugs.
Based on technology, the 3D cell culture market is segmented into scaffold-based and scaffold free systems. The scaffold-based segment is expected to account for the largest share of the global 3D cell culture market in 2016 and is expected to be the fastest-growing segment. Further development of advanced technologies and availability of innovative biodegradable and bioabsorbable materials are favoring the growth of scaffold free technologies in coming years.
Download PDF Brochure:https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=191072847

Based on application, the 3D cell culture market is segmented into cancer cell research, cell based assays/toxicity screening, regenerative medicine/tissue engineering, in vivo applications for stem cells, 3D printing/microfluidics, and others. The cancer cell research segment is poised to witness the highest growth rate in this market due to their increasing adoption as it speeds up the cancer drug discovery process than traditional time-consuming and expensive animal models.
Based on end-user, the 3D cell culture market is segmented into research laboratories & institutes, biotechnology & pharmaceuticals, hospitals & diagnostics centers, and others. The biotechnology & pharmaceuticals segment is poised to witness the highest growth rate in this market due to increasing healthcare expenditure and government investment.
In coming years, regenerative and stem cell research market offer huge potential to the growth of this market. Major players are developing advanced assay kits which will reduce the cost and efforts required in the field of regenerative medicine research such as identification of diseases pathways, and evaluation of potential new drugs.




0 Comments